2015年第75屆美國糖尿病協會(ADA)科學年會正在美國波士頓召開。由北京大學人民醫院內分泌代謝科紀立農教授牽頭的ORBIT研究結果在ADA2015年會最新研究壁報專場(Late Breaking Poster Session)上發布。ORBIT研究全稱“基礎胰島素治療的觀察登記性研究”(Observational Registryfor Basal Insulin Treatment),是中國目前最大的基礎胰島素研究項目之一,旨在評估基礎胰島素在臨床實踐中的使用情況--經口服降糖藥物控製不佳的中國2型糖尿病患者接受基礎胰島素治療6個月後的療效和安全性。以下是研究摘要譯文。
基礎胰島素治療盡管已被證實對2型糖尿病患者有效,但基礎胰島素的啟動通常被延遲。我們報告了中國最大型、為期6個月、旨在評價真實世界二級或三級醫院引入基礎胰島素後治療安全性和血糖控製情況的前瞻性研究結果。
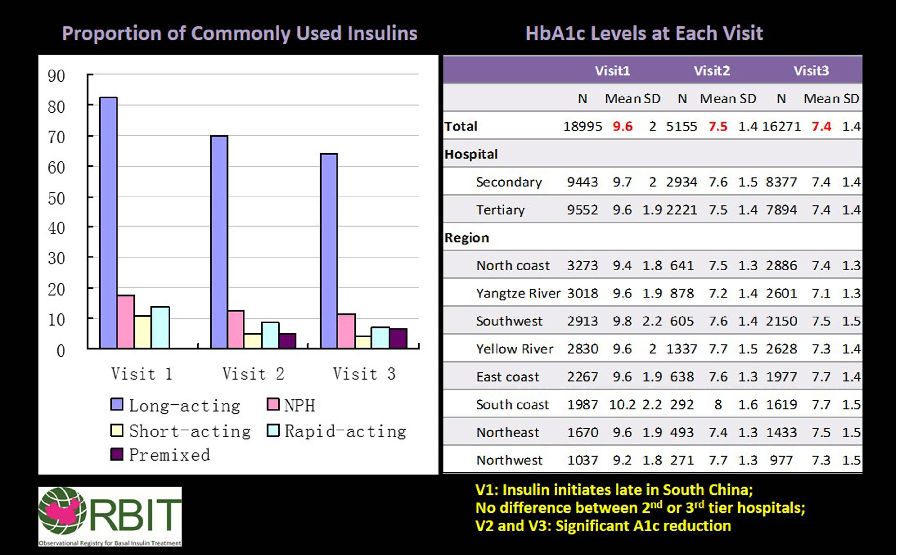
研究納入209家醫院(中國不同地區)口服降糖藥治療但血糖控製不佳(HbA1C≥7%)的成年2型糖尿病患者(n = 18,995),隨訪三次(基線、3個月和6個月)。基礎胰島素的使用類型由醫生判斷。患者平均年齡55.4±10.4歲,糖尿病病程6.4±5.3年(約50%為男性)。
結果顯示,長效基礎胰島素最常用(82.5% - 第一次隨訪,69.9% - 第二次隨訪,64.2%,- 第三次隨訪,圖),各次隨訪中效NPH使用率均<18%。長效基礎胰島素-甘精胰島素的使用率:第一次隨訪時為70%,第二次隨訪時為59%,第三次隨訪時為54%,各次隨訪地特胰島素的使用量<13%。>70%使用甘精胰島素和地特胰島素的患者在整個研究過程中繼續使用同種胰島素。40%的患者在治療的前3個月沒有改變胰島素劑量。
3個月時,HbA1c值顯著改善,在6個月時仍得以維持(下圖)。43%的患者達到了目標FBG(<7.0mmol/ L),41%的患者實現了HbA1c目標(<7%)。長效基礎胰島素低血糖發生率更高,體重無增加。
ORBIT研究結論:真實世界起始基礎胰島素治療3個月和6個月可改善血糖控製。
【研究摘要】
| Abstract Number: | 87-LB |
| Title: | Basal Insulin Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled on Oral Antihyperglycemic Agents: ORBIT Study in China(口服降糖藥控製不佳的2型糖尿病患者的基礎胰島素治療:中國ORBIT研究) |
| Authors: | LINONGJI, PUHONG ZHANG, JIANPING WENG, SATISH K. GARG,Beijing,China,Guangzhou,China,Aurora,CO |
| Abstract: | Basal insulin (BI) treatment is usually delayed in patients with T2DM despite its proven efficacy. We report the largest 6-month prospective study in China to evaluate the safety and glucose control after introduction of BI in real-life in the 2nd or 3rd tier hospitals. Inadequately controlled with OADs (A1C ≥7%), adults (N=18,995) with T2DM were enrolled at 209 hospitals (different regions of China) and had 3 visits (baseline, 3 and 6 months). Type of BI used was at the physician’s discretion. Mean age was 55.4±10.4 years, with 6.4±5.3 diabetes duration (~50% men). Long-acting BI was most commonly used (82.5%-visit 1, 69.9%-visit 2, 64.2%- visit 3; Figure), with intermediate-acting NPH insulin used by <18% at all visits. Long-acting BI-glargine was used by 70% at visit 1, 59% at visit 2, and 54% at visit 3 of patients, whereas detemir was used in <13% at each visit. >70% of glargine and detemir users continued to use the same insulin throughout the study. 40% of patients did not change their insulin dose at all in the first 3 months. There was a significant improvement in A1c values at 3 months, which was maintained at 6 months (Figure). Target FBG (<7.0 mmol/L) and A1C (<7%) were achieved in 43% and 41% of patients, respectively. Hypoglycemia was higher with no weight gain for long-acting BI. We conclude that BI initiation in real-life improves glucose control at 3 and 6 months in the ORBIT study. |